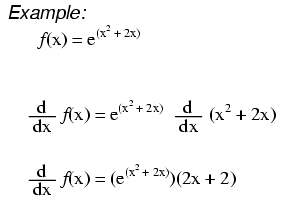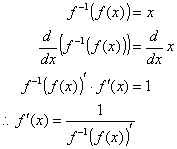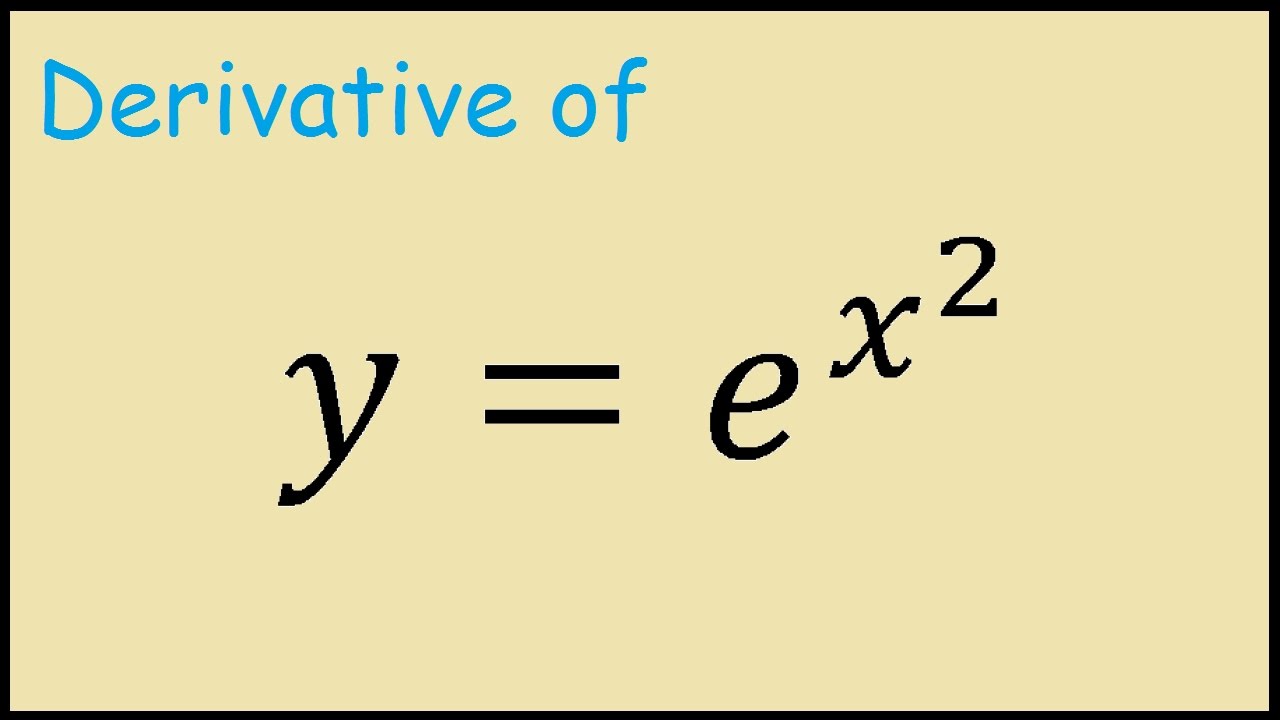Derivative Rules E F X

Endgroup kostasst7 jul 8 14 at 9 44.
Derivative rules e f x. We ve covered methods and rules to differentiate functions of the form y f x where y is explicitly defined as. Begingroup this e 2x is a part of question f x e 2x sin 5x. When the first derivative of a function is zero at point x 0. F x cthenf0 x 0 constant multiple rule.
Then the second derivative at point x 0 f x 0 can indicate the type of that point. Now you can forget for a while the series expression for the exponential. Since the limit of as is less than 1 for and greater than for as one can show via direct calculations and since is a continuous function of for it follows that there exists a positive real number we ll call such that for we get. When applying the chain rule.
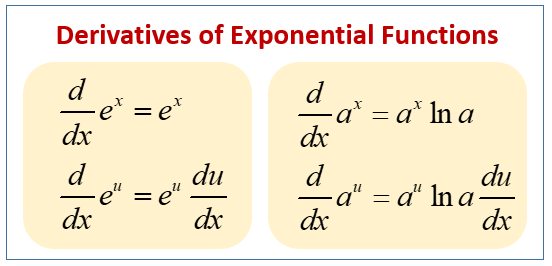
Derivatives of f x a x let s apply the definition of differentiation and see what happens. Do i have to use both rules or just the chain rule to solve this function above. The derivative of e x is e x. We only needed it here to prove the result above.
The slope of a line like 2x is 2 or 3x is 3 etc. F x x 3 5x 2 x 8. See all questions in chain rule. It means the slope is the same as the function value the y value for all points on the graph.
F x 3x 2 2 5x 1 0 3x 2 10x 1 example 2. The slope of a constant value like 3 is always 0. We can now apply that to calculate the derivative of other functions involving the exponential. Derivative examples example 1.
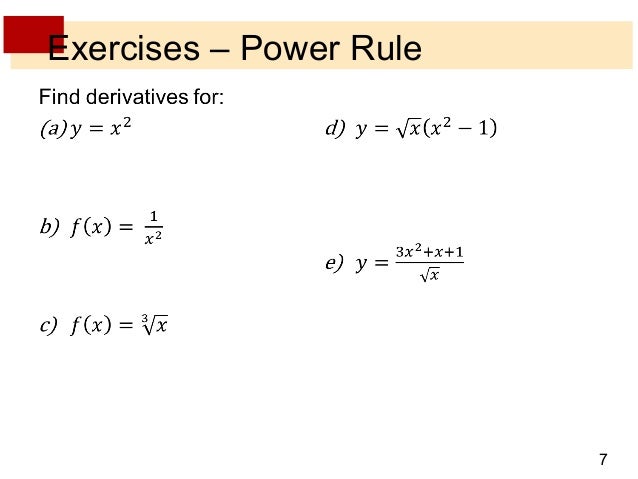
F x 0 0. How do you find the derivative of y x 2 3x 5 1 4. Since the derivative of e x is e x then the slope of the tangent line at x 2 is also e 2 7 39. Here are useful rules to help you work out the derivatives of many functions with examples below.
D e x dx e x what does this mean. At this point the y value is e 2 7 39. F x cos 3x 2 3x 2 cos 3x 2 6x second derivative test. This is one of the properties that makes the exponential function really important.
How do you find the derivative of y 1 x 1 x 3. Read more high school math solutions derivative calculator the chain rule. Let s take the example when x 2. The derivative tells us the slope of a function at any point.